Dynamic nuclear polarization of spherical nanoparticles†
Abstract
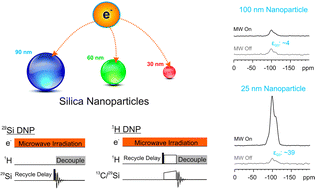
Spherical silica nanoparticles of various particle sizes (∼10 to 100 nm), produced by a modified Stoeber method employing amino acids as catalysts, are investigated using Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (DNP) enhanced Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. This study includes ultra-sensitive detection of surface-bound amino acids and their supramolecular organization in trace amounts, exploiting the increase in NMR sensitivity of up to three orders of magnitude via DNP. Moreover, the nature of the silicon nuclei on the surface and the bulk silicon nuclei in the core (sub-surface) is characterized at atomic resolution. Thereby, we obtain unique insights into the surface chemistry of these nanoparticles, which might result in improving their rational design as required for promising applications, e.g. as catalysts or imaging contrast agents. The non-covalent binding of amino acids to surfaces was determined which shows that the amino acids not just function as catalysts but become incorporated into the nanoparticles during the formation process. As a result only three distinct Q-types of silica signals were observed from surface and core regions. We observed dramatic changes of DNP enhancements as a function of particle size, and very small particles (which suit in vivo applications better) were hyperpolarized with the best efficiency. Nearly one order of magnitude larger DNP enhancement was observed for nanoparticles with 13 nm size compared to particles with 100 nm size. We determined an approximate DNP penetration-depth (∼4.2 or ∼5.7 nm) for the polarization transfer from electrons to the nuclei of the spherical nanoparticles. Faster DNP polarization buildup was observed for larger nanoparticles. Efficient hyperpolarization of such nanoparticles, as achieved in this work, can be utilized in applications such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...