The origin of the strong interfacial charge-transfer absorption in the surface complex between TiO2 and dicyanomethylene compounds
Abstract
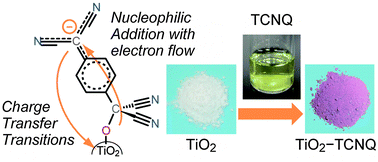
Interfacial charge transfer transitions between organic and inorganic materials are expected to be a potential photoinduced charge separation mechanism for photoenergy conversions. Recently, we reported that the hybrid material formed from TiO2 nanoparticles and an organic electron acceptor, 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ), shows strong interfacial charge transfer absorption in the visible region. In this work, we have theoretically studied the structure, and electronic and absorption properties in order to clarify the formation mechanism and the origin of the strong interfacial charge transfer absorption. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations employing an anatase Ti14O28H2(OH)2(H2O)2 nano-cluster unraveled that the surface complex is formed by a nucleophilic addition reaction between a surface hydroxyl group of TiO2 and the carbon atom of the methylene moiety in TCNQ with the drastic changes in the structure and electronic properties of TCNQ. In the formation process, owing to the high electron affinity of TCNQ, a negative charge of the surface oxygen atom is transferred to the TCNQ moiety. This leads to a significant electronic hybridization between TiO2 and TCNQ, which is the origin of interfacial charge transfer transitions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...