OH-initiated oxidation of sub-micron unsaturated fatty acid particles†
Abstract
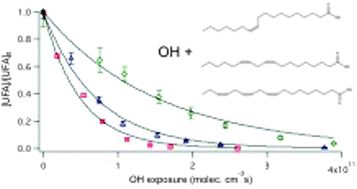
The heterogeneous reaction of OH radicals with sub-micron unsaturated fatty acid particles in the presence of H2O2 and O2 is studied to explore how surface OH addition reactions initiate chain reactions that rapidly transform the chemical composition of an organic particle. In the presence of 20.7 ppm [H2O2] in a 10% mixture of O2 in N2, the effective uptake coefficients of oleic acid, linoleic acid and linolenic acid are found to be 1.72 ± 0.08, 3.75 ± 0.18 and 5.73 ± 0.14, respectively. These effective uptake coefficients are larger than unity, providing clear evidence for particle-phase secondary chain chemistry. The effective uptake coefficient increases linearly with the number of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bonds in the unsaturated fatty acid molecule. Elemental composition analysis reveals that there is an addition of, on average, 0.57 ± 0.02, 0.61 ± 0.01 and 0.73 ± 0.04 O atoms per reactive loss of oleic acid, linoleic acid and linolenic acid, respectively, which suggests that OH addition to the C
C double bonds in the unsaturated fatty acid molecule. Elemental composition analysis reveals that there is an addition of, on average, 0.57 ± 0.02, 0.61 ± 0.01 and 0.73 ± 0.04 O atoms per reactive loss of oleic acid, linoleic acid and linolenic acid, respectively, which suggests that OH addition to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bond is not the sole reaction pathway that consumes the molecular species. These results suggest the potential presence of secondary reactions that consume the unsaturated fatty acid molecular species without increasing the particulate oxygen content. As the unsaturated fatty acid particles become more oxygenated, volatilization also becomes significant. The magnitudes of the effective uptake coefficients are found to be dependent on the concentrations of OH, O2 and H2O2 in the flow reactor. A plausible reaction mechanism is presented to show how surface OH addition reactions initiate chain reactions that rapidly transform an unsaturated organic particle's physicochemical properties.
C double bond is not the sole reaction pathway that consumes the molecular species. These results suggest the potential presence of secondary reactions that consume the unsaturated fatty acid molecular species without increasing the particulate oxygen content. As the unsaturated fatty acid particles become more oxygenated, volatilization also becomes significant. The magnitudes of the effective uptake coefficients are found to be dependent on the concentrations of OH, O2 and H2O2 in the flow reactor. A plausible reaction mechanism is presented to show how surface OH addition reactions initiate chain reactions that rapidly transform an unsaturated organic particle's physicochemical properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...