Frictional forces between hydrophilic and hydrophobic particle coated nanostructured surfaces
Abstract
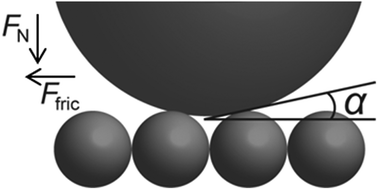
Friction forces have long been associated with the famous Amontons' rule that states that the friction force is linearly dependent on the applied normal load, with the proportionality constant being known as the friction coefficient. Amontons' rule is however purely phenomenological and does not in itself provide any information on why the friction coefficient is different for different material combinations. In this study, friction forces between a colloidal probe and nanostructured particle coated surfaces in an aqueous environment exhibiting different roughness length scales were measured by utilizing the atomic force microscope (AFM). The chemistry of the surfaces and the probe was varied between hydrophilic silica and hydrophobized silica. For hydrophilic silica surfaces, the friction coefficient was significantly higher for the particle coated surfaces than on the flat reference surface. All the particle coated surfaces exhibited similar friction coefficients, from which it may be concluded that the surface geometry, and not the roughness amplitude per se, influenced the measured friction. During measurements with hydrophobic surfaces, strong adhesive forces related to the formation of a bridging air cavity were evident from both normal force and friction force measurements. In contrast to the frictional forces between the hydrophilic surfaces, the friction coefficient for hydrophobic surfaces was found to depend on the surface structure and we believe that this dependence is related to the restricted movement of the three-phase line of the bridging air cavity. For measurements using a hydrophobic surface and a hydrophilic probe, the friction coefficient was significantly smaller compared to the two homogeneous systems. A layer of air or air bubbles on the hydrophobic surface working as a lubricating layer is a possible mechanism behind this observation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...