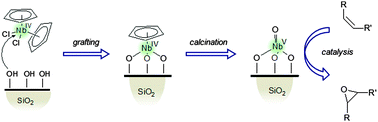
Niobium-containing silica materials obtained by deposition via liquid-phase grafting or dry impregnation of niobocene(IV) dichloride are active and selective catalysts in the epoxidation of alkenes in the presence of aqueous hydrogen peroxide. The generation of the catalytically-active Nb species was followed step-by-step, and investigated using a combined DR-UV-Vis, NIR, Raman, XRD, XANES and EXAFS analyses. At the end of the grafting procedure, the nature of the surface active species can be described as an oxo-Nb(V) site, tripodally grafted onto the silica surface in close proximity to other Nb(V) centres. The liquid-phase methodology provides a better dispersion of the metal sites onto the siliceous support than the dry-impregnation approach. The niobium–silica catalysts were then tested in the epoxidation of cyclohexene and 1-methylcyclohexene, as model substrates.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...