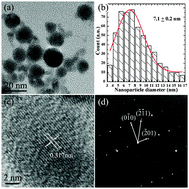
Gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3), which can be used as a T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent, has attracted intense attention in recent years. In this paper, ligand-free monoclinic Gd2O3 nanocrystals of 7.1 nm in diameter are synthesized by a simple and green approach, namely microsecond laser ablation of a gadolinium (Gd) target in deionized water. These nanocrystals obtain high r1 relaxivity of 5.53 s−1 mM−1, and their low toxicity was demonstrated by the cell viability of S18 cells and apoptosis in RAW264.7 cells. In vitro and in vivo MR images show these particles to be good T1-weighted MRI contrast agents. Base on the experimental results and theoretical analysis, we suggest that the purity of the Gd2O3 contributes to its high r1 relaxivity value, while the low toxicity is due to its good crystallinity. These findings show that laser ablation in liquid (LAL) is a promising strategy to synthesize ligand-free monoclinic Gd2O3 nanocrystals for use as high efficient T1-weighted MRI contrast agents.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...