Non-aqueous carbon black suspensions for lithium-based redox flow batteries: rheology and simultaneous rheo-electrical behavior
Abstract
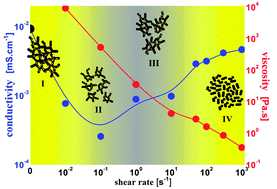
We report on the rheological and electrical properties of non-aqueous carbon black (CB) suspensions at equilibrium and under steady shear flow. The smaller the primary particle size of carbon black is, the higher the magnitude of rheological parameters and the conductivity are. The electrical percolation threshold ranges seem to coincide with the strong gel rather than the weak gel rheological threshold ones. The simultaneous measurements of electrical properties under shear flow reveal the well-known breaking-and-

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...