β-MnO2 as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries from first principles calculations†
Abstract
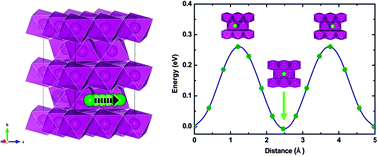
The search for excellent cathodes for lithium batteries is the main topic in order to meet the requirements of low cost, high safety, and high capacity in many real applications. β-MnO2, as a potential candidate, has attracted great attention because of its high stability and potential high capacity among all the phases. Because of the complexity of β-MnO2, some fundamental questions at the atomic level during the charge–discharge process, remain unclear. The lithiation process of β-MnO2 has been systematically examined by first-principles calculations along with cluster expansion techniques. Five stable configurations during the lithium intercalation process are firstly determined, and the electrochemical voltages are from 3.47 to 2.77 eV, indicating the strongly correlated effects of the β-MnO2–LiMnO2 system. During the lithiation process, the changes in the lattice parameters are not symmetric. The analysis of electronic structures shows that Mn ions are in the mixed valence states of Mn3+ and Mn4+ during the lithiation process, which results in Jahn–Teller distortion in Mn3+O6 octahedra. Such results uncover the intrinsic origin of the asymmetric deformation during the charge–discharge process, resulting in the irreversible capacity fading during cycling. From the analysis of the thermal reduction of delithiated LixMnO2, the formation of oxygen is thermodynamically infeasible in the whole extraction process. Our results indicate that β-MnO2 has great potential as a cathode material for high capacity Li-ion batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...