Drug-loaded nanoparticles and supramolecular nanotubes formed from a volatile microemulsion with bile salt derivatives†
Abstract
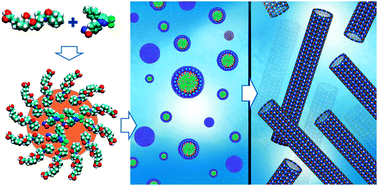
The main objective of this study was to form
* Corresponding authors
a
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Edmond J. Safra campus, Givat Ram, Jerusalem, Israel
E-mail:
magdassi@cc.huji.ac.il
Fax: +972 2 65 84350
Tel: +972 2 65 84967
b
Dipartimento di Chimica, Sapienza Università di Roma, P.le A. Moro 5, 00185 Roma, Italy
E-mail:
l.galantini@caspur.it
Fax: +39 06 490631
Tel: +39 06 4991 3687
c Department of Biotechnology and Food Engineering, Technion—Israel Institute of Technology, 32000 Haifa, Israel
d Departamento de Química Física, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Avda. Alfonso X El Sabio s/n, 27002 Lugo, Spain
e Escuela de Química, Centro de Investigación en Electroquímica y Energía Química (CELEQ), Universidad de Costa Rica, San José, Costa Rica
The main objective of this study was to form

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
K. Margulis-Goshen, M. C. di Gregorio, N. V. Pavel, L. Abezgauz, D. Danino, J. Vázquez Tato, V. H. Soto Tellini, S. Magdassi and L. Galantini, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15, 6016 DOI: 10.1039/C3CP50258A
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
