Towards accurate estimates of the spin-state energetics of spin-crossover complexes within density functional theory: a comparative case study of cobalt(ii) complexes†
Abstract
We report a detailed DFT study of the energetic and structural properties of the spin-crossover Co(II) complex [Co(tpy)2]2+ (tpy = 2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine) in the low-spin (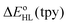 which strongly depend on the functional used. This dependency on the functional was also reported for the DFT estimates of the zero-point energy difference
which strongly depend on the functional used. This dependency on the functional was also reported for the DFT estimates of the zero-point energy difference 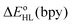 in the HS complex [Co(bpy)3]2+ (
in the HS complex [Co(bpy)3]2+ (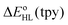 and
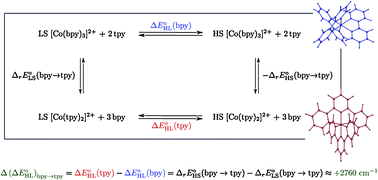
and 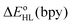 estimates showed that all functionals correctly predict an increase of the zero-point energy difference upon the bpy → tpy
estimates showed that all functionals correctly predict an increase of the zero-point energy difference upon the bpy → tpy 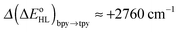 . From these results and basic thermodynamic considerations, we establish that, despite their limitations, current DFT methods can be applied to the accurate determination of the spin-state energetics of complexes of a transition metal ion, or of these complexes in different environments, provided that the spin-state energetics is accurately known in one case. Thus, making use of the availability of a highly accurate ab initio estimate of the HS–LS energy difference in the complex [Co(NCH)6]2+ [L. M. Lawson Daku, F. Aquilante, T. W. Robinson and A. Hauser, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2012, 8, 4216], we obtain for [Co(tpy)2]2+ and [Co(bpy)3]2+ best estimates of
. From these results and basic thermodynamic considerations, we establish that, despite their limitations, current DFT methods can be applied to the accurate determination of the spin-state energetics of complexes of a transition metal ion, or of these complexes in different environments, provided that the spin-state energetics is accurately known in one case. Thus, making use of the availability of a highly accurate ab initio estimate of the HS–LS energy difference in the complex [Co(NCH)6]2+ [L. M. Lawson Daku, F. Aquilante, T. W. Robinson and A. Hauser, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2012, 8, 4216], we obtain for [Co(tpy)2]2+ and [Co(bpy)3]2+ best estimates of 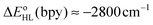 and
and 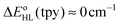 , in good agreement with the known magnetic behaviour of the two complexes.
, in good agreement with the known magnetic behaviour of the two complexes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...