An advanced cathode for Na-ion batteries with high rate and excellent structural stability†
Abstract
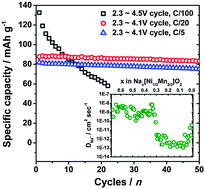
Layered P2-Nax[Ni1/3Mn2/3]O2 (0 < x < 2/3) is investigated as a cathode material for Na-ion batteries. A combination of first principles computation, electrochemical and synchrotron characterizations is conducted to elucidate the working mechanism for the improved electrochemical properties. The reversible phase transformation from P2 to O2 is observed. New configurations of Na-ions and vacancy are found at x = 1/3 and 1/2, which correspond to the intermediate phases upon the electrochemical cycling process. The mobility of Na-ions is investigated using the galvanostatic intermittent

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...