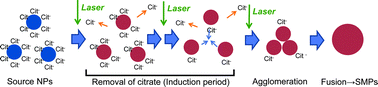
Results of very recent studies have shown that laser irradiation (LI) of colloidal nanoparticles (NPs) using a non-focused laser beam at moderate fluence transforms the NPs to submicron-sized spherical particles (SMPs). For this study, we applied this technique to prepare gold SMPs from source gold NPs prepared by laser ablation of a gold plate in an aqueous solution. Results show that SMPs were obtained from NPs in pure water, but a considerably large amount of the source NPs were sedimented without LI. On the other hand, SMPs were not obtained from NPs stabilized by 1 mM citrate. These findings indicate that the agglomeration of the source NPs prior to the laser-induced melting is important to obtain SMPs, although the sedimentation of the source NPs caused by considerable agglomeration should be reduced to obtain SMPs efficiently. A proper condition of the agglomeration tendency of the source NPs to prepare SMPs reducing the sedimentation of the source NPs was obtainable by simply adjusting the citrate solution concentration. Moreover, investigation of the temporal dynamics of the formation process of SMPs suggested that the agglomeration of the source NPs not only is controlled by citrate but also is induced by LI. LI brings about the decomposition and removal of citrate molecules on the surface of the source NPs, and cause the agglomeration of the source NPs dynamically; then it brings about the fusion of the agglomerated NPs.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...