Nanoparticle translocation through a lipid bilayer tuned by surface chemistry†
Abstract
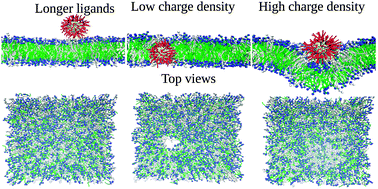
An enhanced understanding about the interactions between nanomaterials and cell membranes may have important implications for biomedical applications. In this work, coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations of gold nanoparticles interacting with lipid bilayers were performed to evaluate the effect of hydrophobicity, charge density and ligand length on lipid bilayers. The simulations accomplished indicate that hydrophobic and anionic nanoparticles do not exhibit significant interactions and different charge densities may induce pore formation or nanoparticle wrapping, resembling first stages of endocytosis. The suggested interplay between charge density and ligand length has important implications when designing nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery applications. Moreover, control of charge densities may induce internalization of nanoparticles into cells through different mechanisms such as passive translocation, for nanoparticles with low charge density, or endocytosis for higher charge densities, highlighting the role of surface chemistry in nanoparticle–cell interactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...