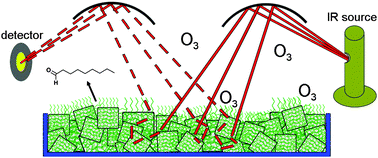
The ozonolysis of 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC) adsorbed on salt mixtures as models for sea-salt particles was studied in real time using diffuse reflection infrared Fourier transform spectrometry (DRIFTS) at room temperature with and without added water vapor. The salt substrates were a mixture of MgCl2·6H2O with NaCl or a commercially available synthetic sea salt. Ozone concentrations ranged from (0.25 to 3.9) × 1013 molecules cm−3 (0.1–1.6 ppm). The major products identified by FTIR and confirmed using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry were the secondary ozonide (SOZ) and a phospholipid aldehyde and carboxylic acid formed by scission of the double bond. The reaction probabilities for the two substrates were similar, γ = (6–7) × 10−7, with an estimated overall uncertainty of a factor of two. The presence of water vapor decreased the yield of SOZ relative to the products formed by C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C scission, but also increased the availability of the double bond for reaction, particularly on the less hygroscopic commercial sea-salt substrate. Thus, water not only affects the mechanisms and products, but also the structure of the phospholipid on the salt in a manner that affects its reactivity. The results of these studies suggest that the reactivity and products of oxidation of unsaturated phospholipids on sea-salt particles in air will be very sensitive to the nature and phase of the substrate, the amount of water present, and whether there is phase separation between the organics and the inorganic salt mixture.
C scission, but also increased the availability of the double bond for reaction, particularly on the less hygroscopic commercial sea-salt substrate. Thus, water not only affects the mechanisms and products, but also the structure of the phospholipid on the salt in a manner that affects its reactivity. The results of these studies suggest that the reactivity and products of oxidation of unsaturated phospholipids on sea-salt particles in air will be very sensitive to the nature and phase of the substrate, the amount of water present, and whether there is phase separation between the organics and the inorganic salt mixture.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C scission, but also increased the availability of the double bond for reaction, particularly on the less hygroscopic commercial sea-salt substrate. Thus,
C scission, but also increased the availability of the double bond for reaction, particularly on the less hygroscopic commercial sea-salt substrate. Thus, 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...