Synthesis, structural versatility, luminescent and magnetic properties of a series of coordination polymers constructed from biphenyl-2,4,4′-tricarboxylate and different N-donor ligands†
Abstract
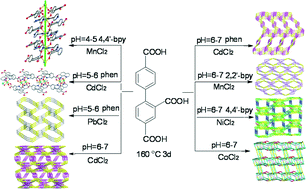
Eight new coordination polymers [Mn(H2btc)2(4,4′-bpy)2]n (1), {[Cd(Hbtc)(phen)(H2O)]·H2O}n (2), [Pb(Hbtc)(phen)]n (3), {[Cd3(btc)2(H2O)5]·4H2O}n (4), {[Cd3(btc)2(phen)2(H2O)]·H2O}n (5), [Mn3(btc)2(2,2′-bpy)2]n (6), {[Ni3(btc)2(4,4′-bpy)2.5(μ2-H2O)(H2O)3]·3H2O}n (7), and {[Co2(btc)(μ3-OH)(μ2-H2O) (8), were assembled from different metal(II) chlorides and biphenyl-2,4,4′-tricarboxylic acid (H3btc) as a main building block, and various aromatic N-donors (phen = 1,10-phenanthroline, 4,4′-bpy = 4,4′-bipyridine, 2,2′-bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine) as supporting ligands. By adjusting the reaction pH, H3btc undergoes a partial deprotonation to give the H2btc− form in 1, and the Hbtc2− moiety in 2 and 3, and the fully deprotonated btc3− form in 4–8. All the products were fully characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. Compounds 1 and 2 possess the double helical chain and wheel chain 1D coordination networks, respectively, which are further extended into the 3D supramolecular architectures via hydrogen bonds. The 2D and 3D metal–organic networks of 6 and 3 were topologically classified, revealing the trinodal 3,6,6-connected and uninodal 4-connected nets with the 3,6,6L3 and sra topologies, respectively. Compounds 4, 5, 7, and 8 feature the very complex 3D metal–organic framework structures, generating either pentanodal 3,4,5,6,6- (4), 3,3,4,5,5- (5), and 4,4,4,5,6-connected (7), or tetranodal 3,5,6,6-connected (8) underlying nets with the hitherto undocumented topologies. The obtained data revealed that different coordination modes of the H2btc−/Hbtc2−/btc3− ligands and the resulting crystal architectures depend on a variety of factors, such as the solution pH and the nature of metal ions and N-donor auxiliary ligands. Magnetic susceptibility measurements indicate that 1 and 8 show a dominating ferromagnetic coupling, while 6 and 7 exhibit an antiferromagnetic coupling between the metal centers. Furthermore, thermal stability of 1–8 and luminescent properties of 2–5 were also studied and discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...