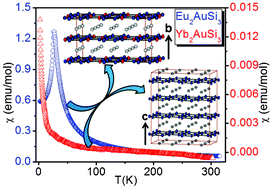
Two new intermetallic compounds Eu2AuSi3 and Yb2AuSi3 having prismatic and rod like shapes, respectively, were grown using indium as inert metal flux. The crystal structure of both compounds was refined using X-ray diffraction data on selected single crystals. Both compounds are ordered variants of the AlB2 structure type and crystallize in the orthorhombic system. Eu2AuSi3 adopts the Ca2AgSi3 structure type, Fmmm space group and lattice parameters a = 8.3060(17) Å, b = 9.0369(18) Å, c = 14.377(3) Å. Yb2AuSi3, on the other hand, crystallizes in the Ba2LiSi3 structure type, Fddd space group and lattice parameters a = 8.2003(16) Å, b = 14.187(3) Å, c = 16.869(3) Å. Both Eu2AuSi3 and Yb2AuSi3 consist of two dimensional hexagonal units built up of [Au3Si3] mixed sites and the europium atoms are sandwiched between two adjacent hexagonal layers. Magnetic measurements suggest both compounds have divalent rare earth atoms. The temperature dependent magnetic susceptibility data of Eu2AuSi3 suggests the Curie–Weiss behavior above 30 K and an antiferromagnetic ordering around 26 K. Yb2AuSi3 is diamagnetic in the higher temperature range (>175 K) and is weakly paramagnetic below 100 K indicating a probable valence fluctuation in Yb.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...