Bioinspired phosphorylcholine containing polymer films with silver nanoparticles combining antifouling and antibacterial properties†
Abstract
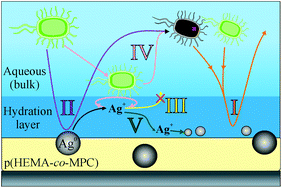
The antibacterial (bioactive) and antifouling (biopassive) properties of stable, uniform, high surface coverage films of poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) (p(HEMA-co-MPC)) with embedded, non-leaching

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...