A facile fabrication of upconversion luminescent and mesoporous core–shell structured β-NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+@mSiO2 nanocomposite spheres for anti-cancer drug delivery and cell imaging†
Abstract
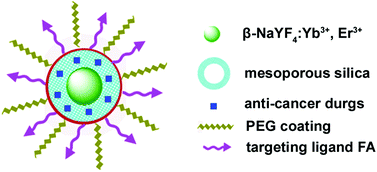
Upconversion luminescent β-NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+ nanoparticles (UCNPs) were encapsulated with uniform mesoporous silica shells, which were further modified with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and cancer-targeting ligand folic acid (FA), resulting in the formation of water-dispersible and biologically functionalized core–shell structured UCNPs@mSiO2 nanoparticles with an overall average size of around 80 nm. The obtained multifunctional nanocomposite spheres can be performed as an anti-cancer drug delivery carrier and applied for cell imaging. It is found that anti-cancer drug doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) can be absorbed into UCNPs@mSiO2-PEG/FA nanospheres and released in a pH-sensitive pattern. In vitro cell cytotoxicity tests on cancer cells verified that DOX-loaded UCNPs@mSiO2-PEG/FA nanospheres exhibited greater cytotoxicity with respect to free DOX and DOX-loaded UCNPs@mSiO2-PEG at the same concentrations, owing to the increase of cell uptake of anti-cancer drug delivery vehicles mediated by the FA receptor. Moreover, the upconversion luminescence image of UCNPs@mSiO2-PEG/FA taken up by cells shows green emission under 980 nm infrared laser excitation, making the UCNPs@mSiO2-PEG/FA nanocomposite spheres promising candidates as bioimaging agents. These findings highlight the promise of the highly versatile multifunctional nanoparticles for simultaneous imaging and therapeutic applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...