Combination of effective machine learning techniques and chemometric analysis for evaluation of Bupleuri Radix through high-performance thin-layer chromatography
Abstract
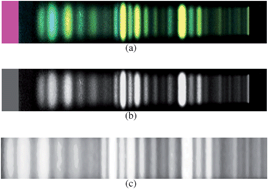
Chaihu (Bupleuri Radix), the root of Bupleurum chinense and B. scorzonerifolium, is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine authenticated in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. There are also several variations available from local herbal markets, for example, the roots of B. falcatum, B. bicaule, and B. marginatum var. stenophyllum. In the current study, we collected 64 Chaihu samples, including 33 authenticated samples and 31 commercial samples. Test solutions of all the examples were analysed by high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) to assess the principal bio-active components (saikosaponins). The HPTLC fluorescent images acquired were analyzed by sophisticated image processing techniques for comprehensive quantification. High dimensional features for both gray-scale and true color images were constructed for the raw images. Classical classification algorithms, including naive Bayes, Support Vector Machine (SVM), K-nearest neighbors, neural network and logistic, were used to construct prediction models. To gain an insight into the principal components while evaluating the Chaihu sample, feature selection and ensemble feature selection methods were further combined with the classifiers to enhance the discrimination power. Ensemble feature selection was shown to achieve superior performance. Experimental results demonstrated that the roots of Chaihu from different species of the genus Bupleurum could be readily distinguished so that commercial samples could be easily classified.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...