Development and validation of a rapid turbidimetric assay to determine the potency of ampicillin sodium in powder for injectable solution
Abstract
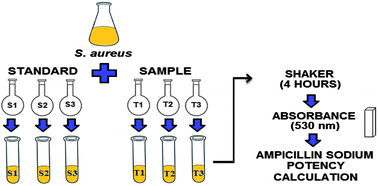
Ampicillin sodium is a β-lactam antimicrobial agent for parenteral use, widely used in many parts of the world and recommended by the World Health Organization. Due to its importance in the treatment of several infectious diseases, the development of optimized analytical methods for the quality control of ampicillin is essential, seeking therapeutic efficacy, patient's safety and also advantages for the pharmaceutical industry. The development of microbiological methods for the analysis of antimicrobials has gained strength in recent years and has been highlighted in relation to physicochemical methods, especially because they make it possible to determine the bioactivity of the drug against a microorganism. In this context, this paper describes the validation of a microbiological method for quantitative analysis of ampicillin sodium in powder for injectable solution by turbidimetric assay. For performing the method, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 26923 was used as the test microorganism and the culture medium chosen was the tryptic soy broth. The method was validated according to ICH guidelines and the results were treated by analysis of variance (ANOVA), showing to be linear (r = 0.9999), precise (RSD values <5.0%), robust and accurate (100.79%), over a concentration range from 2.0 to 8.0 μg mL−1. Furthermore, a Student's t-test showed no statistically significant difference between the proposed turbidimetric method and an HPLC method previously validated. Thus, the validated method is able to quantify ampicillin sodium in powder for injectable solution, while being an economical, rapid and environmentally friendly alternative for its routine analysis in quality control.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...