Retracted Article: Combined microporous membrane-based liquid–liquid–liquid microextraction and in situdifferential pulse voltammetry for highly sensitive detection of trimipramine
Abstract
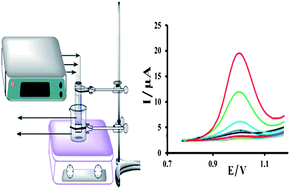
In this paper, a microporous membrane-based liquid–liquid–liquid microextraction and

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...