l-Ascorbic acid biosensing assay from enzyme-immobilized pig bladder membrane as a novel platform
Abstract
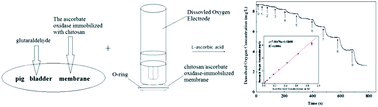
An L-ascorbic acid biosensing assay was developed using the enzyme-immobilized pig bladder membrane and dissolved oxygen electrode. The ascorbate oxidase immobilized with chitosan was bound to bladder membrane by glutaraldehyde as a crosslinking agent. The phosphate buffer (100 mM, pH = 5.0), glutaraldehyde concentration (15%), 0.035 mg enzyme loading, and 20–30 °C were established as the optimum test conditions. This biosensor exhibited a response time of 80 s, a generous linear range of 0.010 mM to 0.88 mM with a detection limit of 10 μM, repeatability (3.1%, n = 20), recoveries (98.7–102%), and good stability with a shelf-life of more than 3 months. The reproducibility of fabrication of the biosensors was investigated by using three different membranes (R.S.D. = 3.0%). The comparison of the analytical performance between the published and the proposed biosensor methods was made. This biosensor has been applied to determine the L-ascorbic acid content in real samples, and the results are in agreement with those obtained by a commercial colorimetric ascorbic acid assay kit.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...