Development and validation of a non-aqueous capillary electrophoresis method for simultaneous estimation of mebendazole and levamisole hydrochloride in compound mebendazole tablets
Abstract
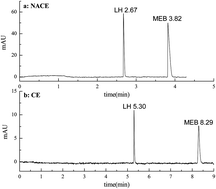
A Non-aqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE) method was employed for the separation of mebendazole and levamisole hydrochloride in compound mebendazole tablets. The optimum separation in NACE, by measuring at 210 nm, was obtained in a 60 cm (50.5 cm effective length) × 75 μm I.D. capillary using a nonaqueous solution system of 40 : 60 (v/v) methanol–acetonitrile containing 10 mmol L−1 ammonium chloride, and applied voltage of 25 kV with hydrodynamic injection. The migration time of levamisole hydrochloride and mebendazole are 2.65 min and 3.78 min, respectively. The linearity of the method was evaluated from 5 to 200 μg mL−1 for each analyte and the correlation coefficient was not less than 0.999. Good results were obtained for different aspects including suitability of the system, linearity, and precision. Detection limits of 0.017 μg mL−1 and 0.022 μg mL−1 were obtained for levamisole hydrochloride and mebendazole. Compared with the aqueous CE, the proposed NACE method has the advantages of shorter separation time and lower detection limits.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...