Combined in situ atomic force microscopy and infrared attenuated total reflection spectroelectrochemistry†
Abstract
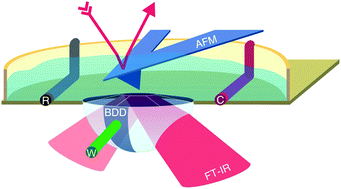
A novel analytical platform combining infrared attenuated total reflection (IR-ATR) spectroelectrochemistry (SE) with atomic force microscopy (AFM) using a boron-doped diamond (BDD)-modified ATR crystal is presented. The utility of this combination is demonstrated investigating the electrodeposition of a polymer film via IR spectroscopy, while the surface modification is simultaneously imaged by AFM. The ATR waveguide consists of a single-crystal intrinsic diamond overgrown with a homoepitaxial BDD layer (thickness: ∼100 nm, boron content: ∼5 × 1020 cm−3) to provide electric conductivity. The diamond ATR crystal is shaped in the form of a hemisphere with a beveled top and an octahedronal surface area of approximately 400 μm2. To demonstrate combined IR-ATR-SE-AFM measurements, the electro-polymerization of 3,4-ethylenedioxothiophene (EDOT) was selected as a model system. Depositions were obtained from aqueous solutions, while changes in IR signature, topography, and electrochemical behavior were recorded in situ and simultaneously during the polymerization process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...