Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of nanomaterials for bioanalysis
Abstract
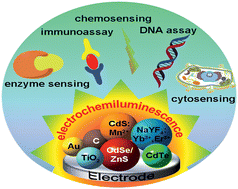
Since the electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) of silicon nanoparticles (NPs) was reported in 2002, miscellaneous nanomaterials with various sizes and shapes have been employed as ECL nanoemitters for bioanalysis. Elucidation of the ECL derivation from these nanoemitters and pertinent biofunctionalization with multitudinous biomolecules can offer excellent ECL signal-transduction platforms for fabricating novel biosensing devices. In this review, we comprehensively describe retrospective and recent advances in NPs-based ECL and related biosensing methodologies, and review their analytical applications in the detection of small biological molecules, enzymatic sensing, immunoassay, DNA analysis and cytosensing.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2013's Top 25 most read Analyst articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...