The relative roles of DNA damage induced by UVA irradiation in human cells†
Abstract
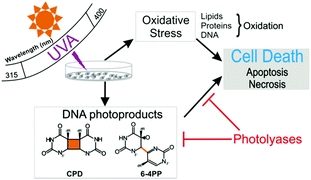
UVA light (320–400 nm) represents approximately 95% of the total solar UV radiation that reaches the Earth's surface. UVA light induces oxidative stress and the formation of DNA photoproducts in skin cells. These photoproducts such as pyrimidine dimers (cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers, CPDs, and pyrimidine (6-4) pyrimidone photoproducts, 6-4PPs) are removed by nucleotide excision repair (NER). In this repair pathway, the XPA protein is recruited to the damage removal site; therefore, cells deficient in this protein are unable to repair the photoproducts. The aim of this study was to investigate the involvement of oxidative stress and the formation of DNA photoproducts in UVA-induced cell death. In fact, similar levels of oxidative stress and oxidised bases were detected in XP-A and NER-proficient cells exposed to UVA light. Interestingly, CPDs were detected in both cell lines; however, 6-4PPs were detected only in DNA repair-deficient cells. XP-A cells were also observed to be significantly more sensitive to UVA light compared to NER-proficient cells, with an increased induction of apoptosis, while necrosis was similarly observed in both cell lines. The induction of apoptosis and necrosis in XP-A cells using adenovirus-mediated transduction of specific photolyases was investigated and we confirm that both types of photoproducts are the primary lesions responsible for inducing cell death in XP-A cells and may trigger the skin-damaging effects of UVA light, particularly skin ageing and carcinogenesis.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Interaction of UV radiation with DNA

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...