Bio-inspired magnetic swimming microrobots for biomedical applications
Abstract
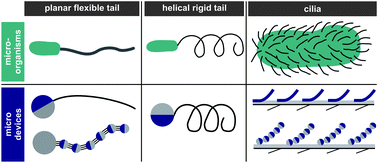
Microrobots have been proposed for future biomedical applications in which they are able to navigate in viscous fluidic environments. Nature has inspired numerous microrobotic locomotion designs, which are suitable for propulsion generation at low Reynolds numbers. This article reviews the various swimming methods with particular focus on helical propulsion inspired by E. coli bacteria. There are various magnetic actuation methods for biomimetic and non-biomimetic microrobots, such as rotating fields, oscillating fields, or field gradients. They can be categorized into force-driven or torque-driven actuation methods. Both approaches are reviewed and a previous publication has shown that torque-driven actuation scales better to the micro- and nano-scale than force-driven actuation. Finally, the implementation of swarm or multi-agent control is discussed. The use of multiple microrobots may be beneficial for in vivo as well as in vitro applications. Thus, the frequency-dependent behavior of helical microrobots is discussed and preliminary experimental results are presented showing the decoupling of an individual agent within a group of three microrobots.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Self-Propelled Nano and Microsystems

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...