Standardless determination of Nd isotope ratios in glasses and minerals using laser-ablation multiple-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with a low-oxide molecular yield interface setup†
Abstract
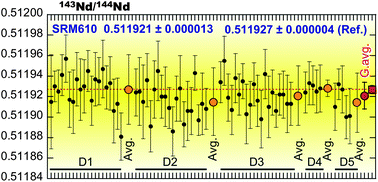
We investigated an appropriate instrumental setup for a laser-ablation multiple-collector

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...