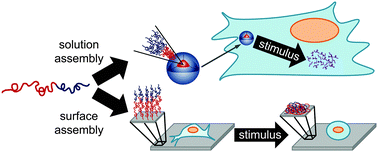
Stimuli-responsive polymeric materials is one of the fastest growing fields of the 21st century, with the annual number of papers published more than quadrupling in the last ten years. The responsiveness of polymer solution assemblies and surfaces to biological stimuli (e.g. pH, reduction–oxidation, enzymes, glucose) and externally applied triggers (e.g. temperature, light, solvent quality) shows particular promise for various biomedical applications including drug delivery, tissue engineering, medical diagnostics, and bioseparations. Furthermore, the integration of copolymer architectures into stimuli-responsive materials design enables exquisite control over the locations of responsive sites within self-assembled nanostructures. The combination of new synthesis techniques and well-defined copolymer self-assembly has facilitated substantial developments in stimuli-responsive materials in recent years. In this tutorial review, we discuss several methods that have been employed to synthesize self-assembling and stimuli-responsive copolymers for biomedical applications, and we identify common themes in the response mechanisms among the targeted stimuli. Additionally, we highlight parallels between the chemistries used for generating solution assemblies and those employed for creating copolymer surfaces.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...