High current density via direct electron transfer by the halophilic anode respiring bacterium Geoalkalibacter subterraneus†
Abstract
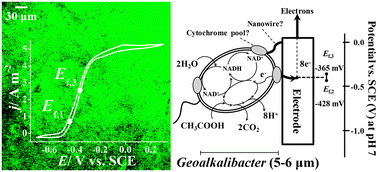
In this study the characterization of Geoalkalibacter subterraneus is presented, which is a novel halophilic anode respiring bacterium (ARB) previously selected and identified in a potentiostatically controlled bioelectrochemical system (BES) inoculated with sediments from a salt plant. Pure culture electroactive biofilms of Glk. subterraneus were grown during chronoamperometric batch experiments at a graphite electrode poised at +200 mV (vs. SCE) with 10 mM acetate as the electron donor. These biofilms exhibited the highest current density (4.68 ± 0.54 A m−2) reported on a planar material with a pure culture under saline conditions (3.5% NaCl). To investigate possible anodic electron transfer (ET) mechanisms, cyclic voltammetry (CV) of mature visible apparent reddish biofilms was performed under bioelectrocatalytic substrate consumption (turnover) and in the absence of the substrate (non-turnover). CV evidenced a well defined typical sigmoidal shape and a pair of clear redox couples under turnover and non-turnover conditions, respectively. Moreover, the calculation of their formal potentials indicated the presence of a common ET mechanism present in both CV conditions between −427.6 ± 0.5 (Ef,2) and −364.8 ± 4.5 mV (Ef,3). Confocal laser scanning microscopy inspection showed a biofilm structure composed of several layers of metabolically active bacteria that spread all over the electrode material within a biofilm up to 76 ± 7 μm thick. Such high value compared to the thickness values normally reported in the literature for pure culture electroactive bacteria justifies further investigations. Taken together, these results suggest that Glk. subterraneus performs a direct ET mechanism in contact with the electrode material. Furthermore, direct current generation from saline wastewater significantly expands the application of BESs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...