Characterization of Pt-doped SnO2 catalyst for a high-performance micro gas sensor
Abstract
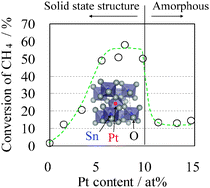
The atomic scale structure and its dependence on Pt concentration of a Pt-doped SnO2 (Pt–SnO2) thin film produced by a sputter-deposition method was investigated, which showed high-performance as a methane gas sensor. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses showed that Pt–SnO2 has a rutile structure similar to SnO2 crystals at less than 10 at% Pt where the Pt ion was located at the Sn position in the rutile structure. There was no evidence that Pt metal clusters were formed in the Pt–SnO2 films. The Pt–SnO2 structure became amorphous at greater than 11 at% Pt. We found a good correlation between the methane activity and local structure of Pt.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...