Aromatic peptide amphiphiles: significance of the Fmoc moiety†
Abstract
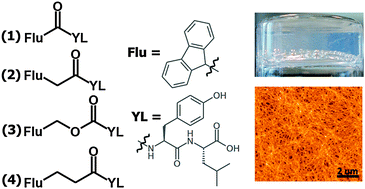
Aromatic peptide amphiphile hydrogelators commonly utilise the fluorenyl-9-methoxycarbonyl moiety as an N-terminal capping group. Material properties and spectroscopic techniques show the influence of alternative linkers between the fluorenyl moiety and the peptide. This study establishes whether methoxycarbonyl is an optimal or mainly convenient linker, for this class of self-assembling systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...