In vitro detection of calcium in bone by modified carbon dots†
Abstract
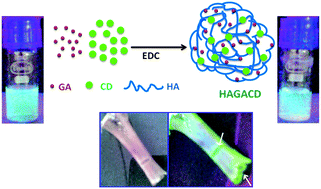
This article depicts a simple and novel approach to locate calcium deposits in bone using modified carbon dots (CDs) through fluorescence imaging. Amino-functionalized CDs along with glutamic acid, a naturally-occurring ligand for calcium ions, were conjugated onto hyaluronic acid using EDC chemistry. The ability of the probe to recognise Ca ions was demonstrated using polymer strips doped with Ca ions and freshly collected bones. The probe was found to bind more at bone cracks, reflecting its potential to locate micro-cracks in bone as well as to map Ca deposits. The bound portions can be visualized through a fluorescence microscope or by illumination by a UV source (365 nm). The components used to generate the probes, namely CD, glutamic acid and hyaluronic acid, are well known for their non-toxicity and biocompatibility. It appears, therefore, that the probe could be used for in vivo applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...