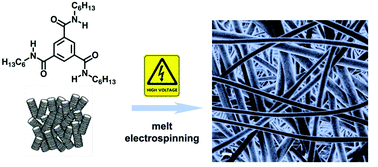
Self-assembling small molecules is considered a promising technology for fabricating micro- and nanosized features. Utilization of typical top-down approaches, such as electrospinning, is rare in combination with self-assembly. Here we report for the first time on melt electrospinning of 1,3,5-cyclohexane- and 1,3,5-benzenetrisamides into fibres. The fibre spinning conditions were investigated with respect to the type of mesophase and applied field strength. It is possible to electrospin fibres from the nematic liquid crystalline phase and, most surprisingly, also from the optical isotropic state slightly above the clearing temperature, but not from columnar LC phases. Under optimized conditions it is possible to prepare homogeneous fibres with diameters below 1 μm.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...