Measuring the elastic modulus of microgels using microdrops
Abstract
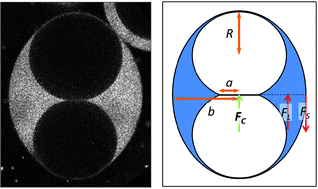
Two microgel particles are encapsulated in a microdrop having a spherical diameter smaller than the sum of the diameters of the microgels; this causes the microgels to be squeezed together by the oil–water interface of the drop, in turn, making the drop ellipsoidal in shape. By modeling the force applied to the microgels by the drop and equating this to the Hertz contact force of their deformation, we are able to estimate their elastic modulus. By varying the surface tension and shape of the drops, we are able to measure the modulus of the microgels under different loads. This provides a simple technique for quantifying the elasticity of small, deformable objects, including liquid drops, microgels, and cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...