Capillary bond between rod-like particles and the micromechanics of particle-laden interfaces†
Abstract
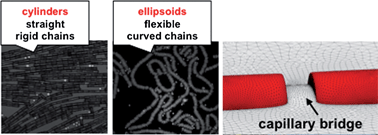
Rod-like microparticles assemble by capillarity at fluid interfaces to make distinctively different microstructures depending on the details of the particle shape. Ellipsoidal particles assemble in side-to-side orientations to form flexible chains, whereas cylinders assemble end-to-end to form rigid chains. To understand these differences, we simulate the near-field capillary interactions between pairs of rod-like particles subject to bond-stretching and bond-bending deformations. By comparing ellipsoids, cylinders, and cylinders with smooth edges, we show that geometric details dramatically affect the magnitude and shape of the capillary energy landscape. We relate this energy landscape to the mechanics of the chains, predicting the flexural rigidity for chains of ellipsoids, and a complex, non-elastic response for chains of cylinders. These results have implications in the design of particle laden interfaces for emulsion stabilization and encapsulation, and for oriented

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...