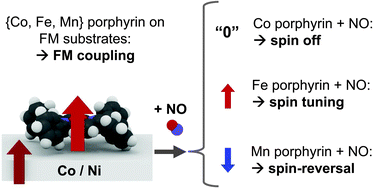
Paramagnetic transition-metal complexes assembled on surfaces are of great interest for potential applications in organic spintronics. The magnetochemical interactions of the spin of the metal centers with both ferromagnetic surfaces and optional axial ligands are yet to be understood. We use a combination of X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) and quantum-chemical simulations based on density functional theory (DFT + U) to investigate these metal–organic interfaces with chemically tunable magnetization. The interplay between an optional axial ligand (NO, spin S = 1/2 or NH3, S = 0) and Ni and Co ferromagnetic surfaces affecting the spin of Co(II) tetraphenylporphyrin (d7, S = 1/2), Fe(II) tetraphenylporphyrin (d6, S = 1), Mn(II) tetraphenylporphyrin (d5, S = 5/2) and Mn(II) phthalocyanine (d5, S = 3/2) is studied. We find that the structural trans effect on the surface rules the molecular spin state, as well as the sign and strength of the exchange interaction with the substrate. We refer to this observation as the surface spin-trans effect.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...