Enhanced performance of core-shell-like structure Zr-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics prepared by a flame synthetic approach
Abstract
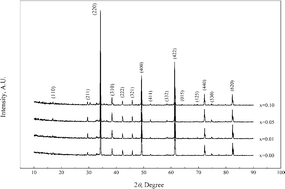
Zr-substituted CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics were fabricated by a sol–gel flame synthetic approach. The influence of microstructure on the dielectric response of the ceramics has been investigated. It is found that CaCu3Ti4−xZrxO12 ceramics with a core-shell-like structure are obtained up to x = 0.05, and the thickness of the interphase region decreases with increasing Zr content. The maximum dielectric constant value is up to ∼6 × 104 for x = 0.05 at 1 kHz at room temperature. The high dielectric constant is connected to grain boundary effects, and the enhanced giant dielectric response with Zr substitution is attributed to a locally stretched lattice near Zr on the B-site and the resulting polarization switching of electric dipole moments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...