Pore length control of mesoporous Co3O4 and its influence on the capacity of porous electrodes for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
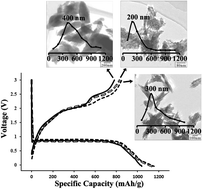
Porous electrodes commonly exhibit much higher charge–discharge capacities than normal electrodes due to their large surface areas. Some factors such as pore size (pore diameter) and wall thickness also influence the electrochemical behavior of porous electrodes in lithium-ion batteries (e.g. the rate of Li-ion intercalation). Here we investigated how the pore length influenced the charge–discharge capacities by using mesoporous Co3O4 with various particle sizes synthesised via controlling the particle size of SBA-15 templates. The capacity and rate capability of porous Co3O4 were increased with

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...