Efficient synthesis of poly(2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate)-silica colloidal nanocomposite particles via aqueous dispersion polymerization†
Abstract
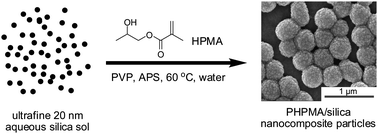
Colloidally stable poly(2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate)-silica nanocomposite particles can be efficiently prepared by aqueous

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...