Degradation of 4-chlorophenol in aqueous solution photoinduced by Fe(iii)–citrate complex
Abstract
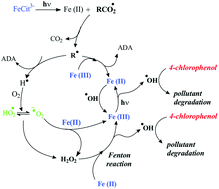
The 4-chlorophenol (4-CP) degradation photoinduced by Fe(III)–citrate complex was investigated upon irradiation at 365 nm at different pHs (2.0, 3.0, 4.0 and 6.0). The best efficiency for 4-CP degradation in the presence of Fe(III)–citrate was at pH 3.0 with a value of quantum yield equal to 0.026. This effect is mainly attributed to speciation of Fe(III)–citrate complex which is very sensitive to the pH. Quantum yields of 4-CP degradation, Fe(III)–citrate disappearance and Fe(II) formation were carried out at wavelength 365 nm at different pHs (3.0 and 6.0). The effect of the pH is less pronounced for the quantum yields of 4-CP than for Fe(III)–citrate complex and Fe(II) quantum yields which are species involved in the initial photochemical process. The effect of oxygen, isopropanol and Fe(III)–citrate concentrations on the quantum yields of 4-CP degradation and also on kinetics of 4-CP disappearance was also studied. Indeed, 4-CP requires the presence of oxygen to be degraded. The disappearance of 4-CP was totally inhibited without oxygen dissolved in the solution. Oxygen is essential for the formation of oxidative species and, as a consequence, for the degradation of the pollutant.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...