Construction of ratiometric fluorescent sensors by ribonucleopeptides†
Abstract
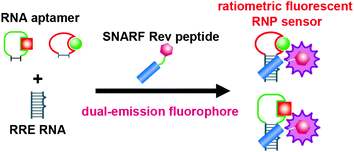
Ratiometric fluorescent sensors were constructed from RNA aptamers by generating modular ribonucleopeptide complexes. Fluorescent ribonucleopeptides containing fluorophore seminaphthorhodafluor tethered to their peptide subunit revealed a dual emission property, which permitted a ratiometric fluorescent measurement of a substrate-binding event. The strategy successfully afforded ratiometric fluorescent sensors for biologically active small
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nucleic acids: new life, new materials

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...