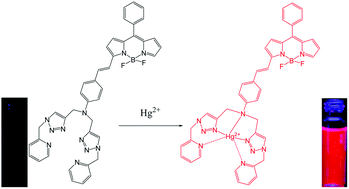
A new monostyryl boron dipyrromethene derivative (MS1) appended with two triazole units indicates the presence of Hg2+ among other metal ions with high selectivity by color change and red emission. Upon Hg2+ binding, the absorption band of MS1 is blue-shifted by 29 nm due to the inhibition of the intramolecular charge transfer from the nitrogen to the BODIPY, resulting in a color change from blue to purple. Significant fluorescence enhancement is observed with MS1 in the presence of Hg2+; the metal ions Ag+, Ca2+, Cd2+, Co2+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, K+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+ cause only minor changes in the fluorescence of the system. The apparent association constant (Ka) of Hg2+ binding in MS1 is found to be 1.864 × 105 M−1. In addition, fluorescence microscopy experiments show that MS1 can be used as a fluorescent probe for detecting Hg2+ in living cells.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...