Elucidation of post-PKS tailoring steps involved in landomycin biosynthesis†
Abstract
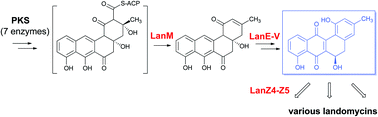
The functional roles of all proposed enzymes involved in the post-PKS redox reactions of the biosynthesis of various landomycin aglycones were thoroughly studied, both in vivo and in vitro. The results revealed that LanM2 acts as a dehydratase and is responsible for concomitant release of the last PKS-tethered intermediate to yield prejadomycin (10). Prejadomycin (10) was confirmed to be a general pathway intermediate of the biosynthesis. Oxygenase LanE and the reductase LanV are sufficient to convert 10 into 11-deoxylandomycinone (5) in the presence of NADH. LanZ4 is a reductase providing reduced flavin (FMNH) co-factor to the partner enzyme LanZ5, which controls all remaining steps. LanZ5, a bifunctional oxygenase–dehydratase, is a key enzyme directing landomycin biosynthesis. It catalyzes hydroxylation at the 11-position preferentially only after the first glycosylation step, and requires the presence of LanZ4. In the absence of such a glycosylation, LanZ5 catalyzes C5,6-dehydration, leading to the production of anhydrolandomycinone (8) or tetrangulol (9). The overall results provided a revised pathway for the biosynthesis of the four aglycones that are found in various congeners of the landomycin group.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...