Fluorogenic sensing of CH3CO2− and H2PO4− by ditopic receptor through conformational change†
Abstract
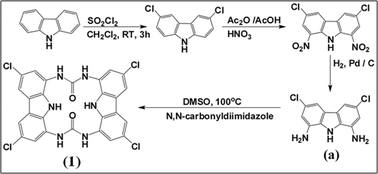
Cyclo-bis-(urea-3,6-dichlorocarbazole) (1) forms a 1 : 2 complex with CH3CO2− and H2PO4− through hydrogen bonding with the two urea moieties, resulting in fluorescence enhancement via a combined photoinduced

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...