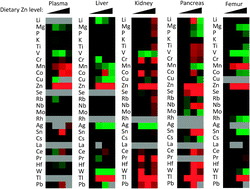
To date, minerals of interest have been analyzed individually to understand mineral dynamics and metabolism. Our recent development of metallomic analyses enabled us to evaluate minerals in an unbiased and global manner. Here, we evaluated the effects of ingestion of excess zinc to plasma and tissue concentrations of minerals in growing rats. A total of 26 minerals were simultaneously evaluated by metallomic analyses using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) in semi-quantification mode; the concentrations of several minerals exhibited consistent changes in response to the concentrations of dietary zinc. Manganese concentrations in plasma and femur increased, while concentrations in the liver and pancreas decreased with increasing dietary zinc concentrations. Because the interaction between zinc and manganese is not known, we further focused our analysis on liver manganese. Quantitative analyses also indicated that the hepatic concentration of manganese decreased in response to the ingestion of diets containing excess zinc, a result that is partly explained by the decreased expression of hepatic Zip8, a manganese transporter. The present study reveals mineral interaction by using metallomic analyses and proposes a possible mechanism that underlies this novel interaction.