An in vivo highly antitumor-active tetrazolato-bridged dinuclear platinum(ii) complex largely circumvents in vitro cisplatin resistance: two linkage isomers yield the same product upon reaction with 9-ethylguanine but exhibit different cytotoxic profiles†
Abstract
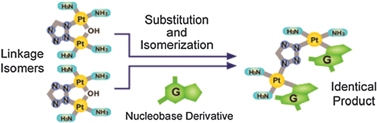
Cytotoxicity assays of azolato-bridged dinuclear Pt(II) complexes, [{cis-Pt(NH3)2}2(μ-OH)(μ-azolato)]2+, where the azolato was pyrazolato (1), 1,2,3-triazolato-N1,N2 (2), tetrazolato-N1,N2 (3), or tetrazolato-N2,N3 (4), were performed in cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant human non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines (PC-9 and PC-14). These complexes largely circumvented the cisplatin resistance in both cell lines, with resistance factors for 1–4 in the range of 0.5–0.8 and 0.9–2.0 for PC-9 and PC-14 cells, respectively. Complex 4 exhibited approximately 10 times the cytotoxicity of 3. When 3 and 4 were reacted with 2 molar equiv. of
- This article is part of the themed collection: Metals and Genetics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...