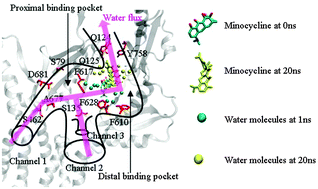
Tripartite complex AcrB–ToIC, the major efflux system in Escherichia coli, is the principal multidrug transporter in Gram-negative bacteria, which is important in antibiotic drug tolerance. AcrB is a homotrimer that acts as a tripartite complex with the outer membrane channel ToIC and the membrane fusion protein AcrA. Recently, the crystal structures of AcrB bound to the high-molecular-mass drugs rifampicin and erythromycin were reported. Here we performed 20 ns molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of the AcrB–rifampicin–minocycline complex in a lipid bilayer and explicit water. We found that the bound drugs, rifampicin and erythromycin, made a unidirectional peristaltic movement towards the extrusion funnel of ToIC, which was facilitated by the water efflux in the channel of AcrB. With a shift of the Phe-617 loop, rifampicin in the access monomer moved towards the entrance of the distal binding pocket. Minocycline in the binding monomer moved from the distal binding pocket towards the gate of the central funnel. The channel between the entrance and the gate made a concerted opening during the MD simulations, which was helpful for the peristaltic movement. Our results showed that the mutations of Gly616Pro and Gly619Pro prevented the movement of the Phe-617 loop, which indicated the critical role of the flexibility of the Phe-617 loop. In addition, three putative proton translocation channels were proposed based on our results. Our study provided dynamical information and important residues for the peristaltic movement in AcrB, which were critical for substrate uptake and extrusion function.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...