The serum metabolomic study of intervention effects of the traditional Chinese medicine Shexiang Baoxin Pill and a multi-component medicine polypill in the treatment of myocardial infarction in rats
Abstract
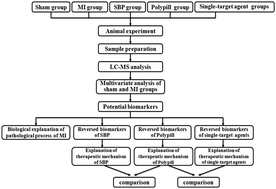
A metabolomic approach based on liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight detector (LC-Q-TOF/MS) was developed to investigate the therapeutic mechanism of a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formula Shexiang Baoxin Pill (SBP) and a multi-component medicine polypill (consisting of simvastatin (Sim), atenolol (Ate), ramipril (Ram), hydrochlorthiazide (Hyd) and aspirin (Asp), named as SARHA). Twenty-seven biomarkers were identified in the serum of MI rats. Thirteen related pathways and 4 main pathological processes including oxidative injury, energy metabolism dysfunction, amino acid metabolism dysfunction and inflammation are involved in MI development. Our study revealed that SBP showed better therapeutic effectiveness than the polypill on MI through regulation of the energy metabolism dysfunction, oxidative injury and inflammation. The combination agent polypill had only certain therapeutic effects on inhibiting oxidative injury and inflammation induced by MI. The reverse effect of the polypill on biomarkers related to MI was much better than mono-therapy groups.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...