PLMLA: prediction of lysine methylation and lysine acetylation by combining multiple features†
Abstract
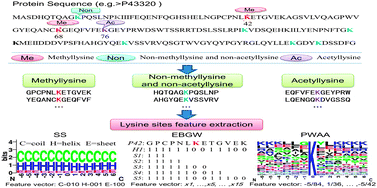
Post-translational lysine methylation and acetylation are two major modifications of lysine residues. They play critical roles in various biological processes, especially in gene regulation. Identification of protein methylation and acetylation sites would be a foundation for understanding their modification dynamics and molecular mechanism. This work presents a method called PLMLA that incorporates protein sequence information, secondary structure and amino acid properties to predict methylation and acetylation of lysine residues in whole protein sequences. We apply an encoding scheme based on grouped weight and position weight amino acid composition to extract sequence information and physicochemical properties around lysine sites. The prediction accuracy for methyllysine and acetyllysine are 83.02% and 83.08%, respectively. Feature analysis reveals that methyllysine is likely to occur at the coil region and acetyllysine prefers to occur at the helix region of protein. The upstream residues away from the central site may be close to methylated lysine in three-dimensional structure and have a significant influence on methyllysine, while the positively charged residues may have a significant influence on acetyllysine. The online service is available at http://bioinfo.ncu.edu.cn/inquiries_PLMLA.aspx.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...